

- PYTHON SERIAL LIBRARY RESET HOW TO
- PYTHON SERIAL LIBRARY RESET SOFTWARE
- PYTHON SERIAL LIBRARY RESET CODE
- PYTHON SERIAL LIBRARY RESET PASSWORD
You can avoid this by either starting the serial connection and storing the handle to the connection as a member variable or taking it as a callback parameter (preferred) or by disabling the auto-restart function.# storing alphabet letter to use thm to crack password Establishing the serial connection is resetting your arduino, and then it's resetting while you perform the serial write so it doesn't realize you're expecting a response when you get to the serial read. In summary, it looks like you're restarting your serial connection in every execute callback. You can just pull out the resistor when you want auto-reset back. Don't go below 110 ohms or above 124 ohms, and don't do this with an isp programmer attached. 120 is hard to find so just combine resistors. Stick a 120 ohm resistor in the headers between 5v and reset (you can find these on the isp connector too).
PYTHON SERIAL LIBRARY RESET SOFTWARE
The simple way that doesn't require any permanent modifying of your hardware or software configuration changes:
PYTHON SERIAL LIBRARY RESET HOW TO
Links can rot, so in the interest of future visitors I'll quote a subset of the page here, describing how to use a pull-up resistor on the reset pin to disable the auto-reset: The answer there also links here for instructions on disabling the auto-reset-on-serial-connection feature. There's a longer explanation about the behavior over at Arduino.SE that says, in part, The way I read this makes it look like you're starting a serial connection repeatedly. įound what I believe is a relevant answer here, and I think it's relevant because of the following lines in your serial_server.py file: When it has been initialized, it'll start executing the following callback. (more)įor the sake of an answer to newcomers struggling with ROS, here is the answer I was given at. #TODO: THIS SECTION HANGS, NEED TO FIGURE HOW TO FIX IT. Self.get_logger().info('Feedback: '.format(i)) #Get feedback to see if we're close to our goal.Īrduino = serial.Serial(port="/dev/ttyUSB0")Īrduino.write(bytes(str("forward"), 'utf-8')) Self.get_logger().info('Executing goal.') #Set the logger to indicate we're starting to execute our goal. #When it has been initialized, it'll start executing the following callback. #Declare it'll be an ActionServer that publishes to the topic 'botmove'. #Declare the Node with the name "serial server". #Class that encapsulates the Action Server. #Action to send commands to the Arduino until it reaches the desired coordinates. FOR DEBUGGING.įrom code_interfaces.action import Fibonacci #Library required to generate a ROS2 Node. #Elements required to generate an ActionServer. #Import the Serial library to send commands to Arduino. The arduino_comm serial_server.py dedicated to sending commands to the Arduino to follow. #Feedback message about current position.
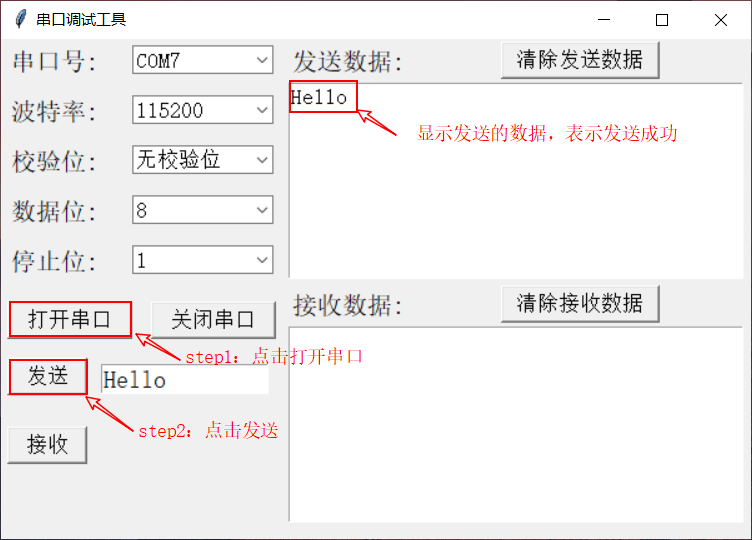
#Resulting position that we're aiming to attain. #Action that sends robot towards a specific spatial position. The Server and Client use the following action, which is based on the tutorial # Initialize BUILTIN LED to light up for feedback.
PYTHON SERIAL LIBRARY RESET CODE
Also I wanted to understand the code I'm working with at its bare basics before adding more complexity with an external library.Īrduino code //Variable to store the bot command. Still operational but sadly seems incompatible with the rosserial and I've checked the Micro-Ros packages and they also seem incompatible with my old arduino. I have an old Arduino Nano that I've had for like 7 years ago that uses the old legacy bootloader. The motor interface provides the action that is used by the arduino_comm package to send serial data. I created a project with the goal of controlling an Arduino using python serial in a workspace with the following structure: - workspace It runs on an Ubuntu 21.04 圆4 machine with kernel 5.8.0-59-generic. I'm using ROS2 foxy with no libraries installed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
